Understanding the Core of PHP Data Structures
Arrays are a fundamental building block in PHP, and mastering them is a critical step for any aspiring web developer. According to W3Techs, as of late 2023, PHP is used by 77.4% of all the websites whose server-side programming language we know. This widespread use makes proficiency in its core features, like arrays, absolutely essential. An array is a special type of variable designed to hold more than one value at a time, organized in a list-like structure. This allows you to group related items together, making your code more organized and efficient. PHP supports three primary types of arrays, each serving a different purpose: indexed arrays, which use numeric keys for ordering; associative arrays, which use named, descriptive keys; and multidimensional arrays, which are essentially arrays that contain other arrays. Understanding how to create, manipulate, and iterate over these powerful data structures is a cornerstone of effective PHP programming and will unlock more advanced capabilities.
Indexed Arrays: The Ordered List
Creating an Indexed Array
Indexed arrays are the simplest form of arrays in PHP. They store a collection of values in a linear sequence, and each value is assigned a numeric index, which automatically starts at zero. Think of it like a numbered list where the first item is at position 0, the second at position 1, and so on. This makes them ideal for storing ordered data, such as a list of product names, user IDs, or daily temperature readings. Creating one is straightforward, and their predictable structure makes them easy to loop through using standard for or foreach loops.
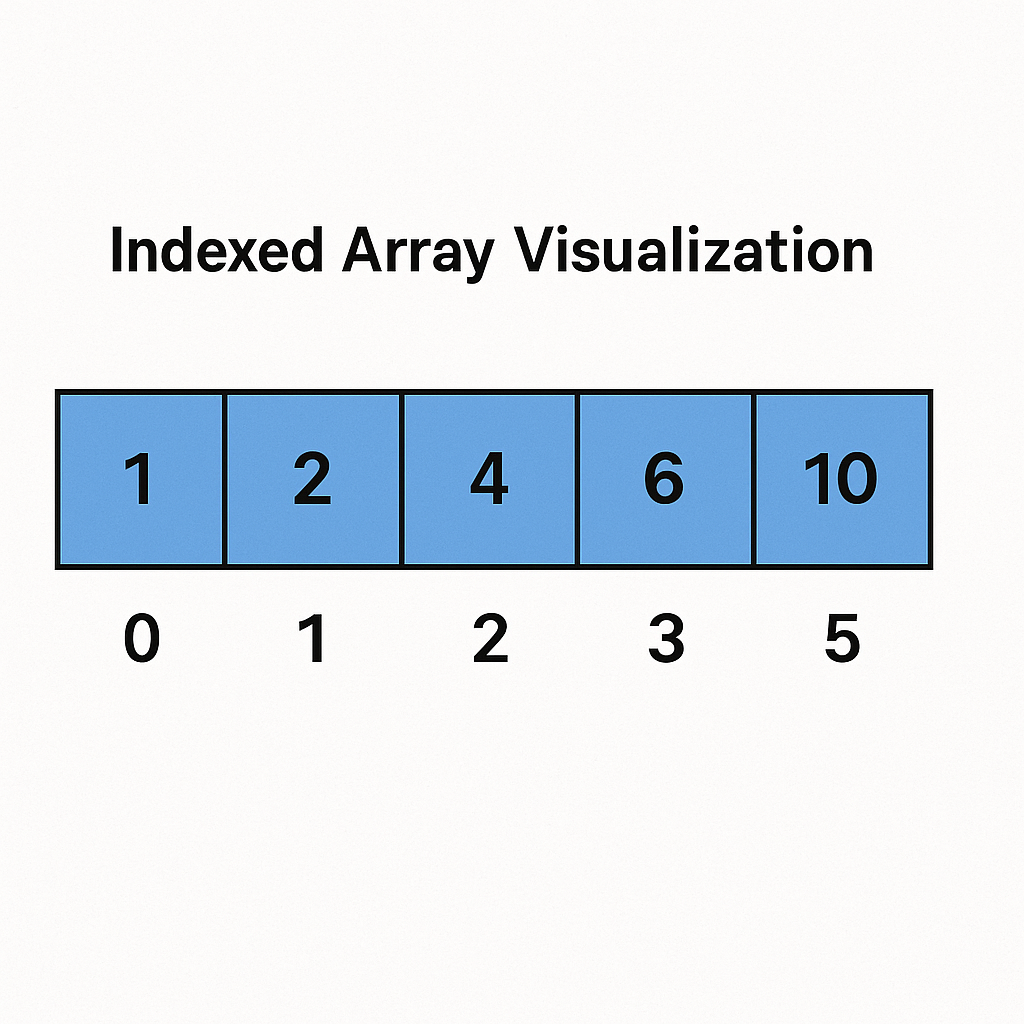
Accessing and Modifying Elements
Once you have an indexed array, you’ll need to interact with its elements. Accessing a specific value is done by referencing its index inside square brackets. For example, to get the first element, you would use its index of 0. Modifying an existing element is just as simple; you just assign a new value to that specific index. Adding a new element to the end of the array is even easier. You can use empty square brackets, and PHP will automatically append the new value with the next available numeric index, saving you the trouble of tracking the array’s length manually.
Associative Arrays: Key-Value Pairs
Defining Associative Arrays
While indexed arrays are great for ordered lists, associative arrays provide a more descriptive and meaningful way to store data. Instead of using numeric indices, you assign a custom string key to each value, creating a collection of key-value pairs. This is incredibly useful for storing data that has a clear relationship, such as the properties of an object. For instance, you could store a user’s information with keys like ‘firstName’, ‘lastName’, and ’email’. This self-documenting structure makes your code much more readable and easier to maintain than trying to remember that index 0 is the first name and index 2 is the email address.
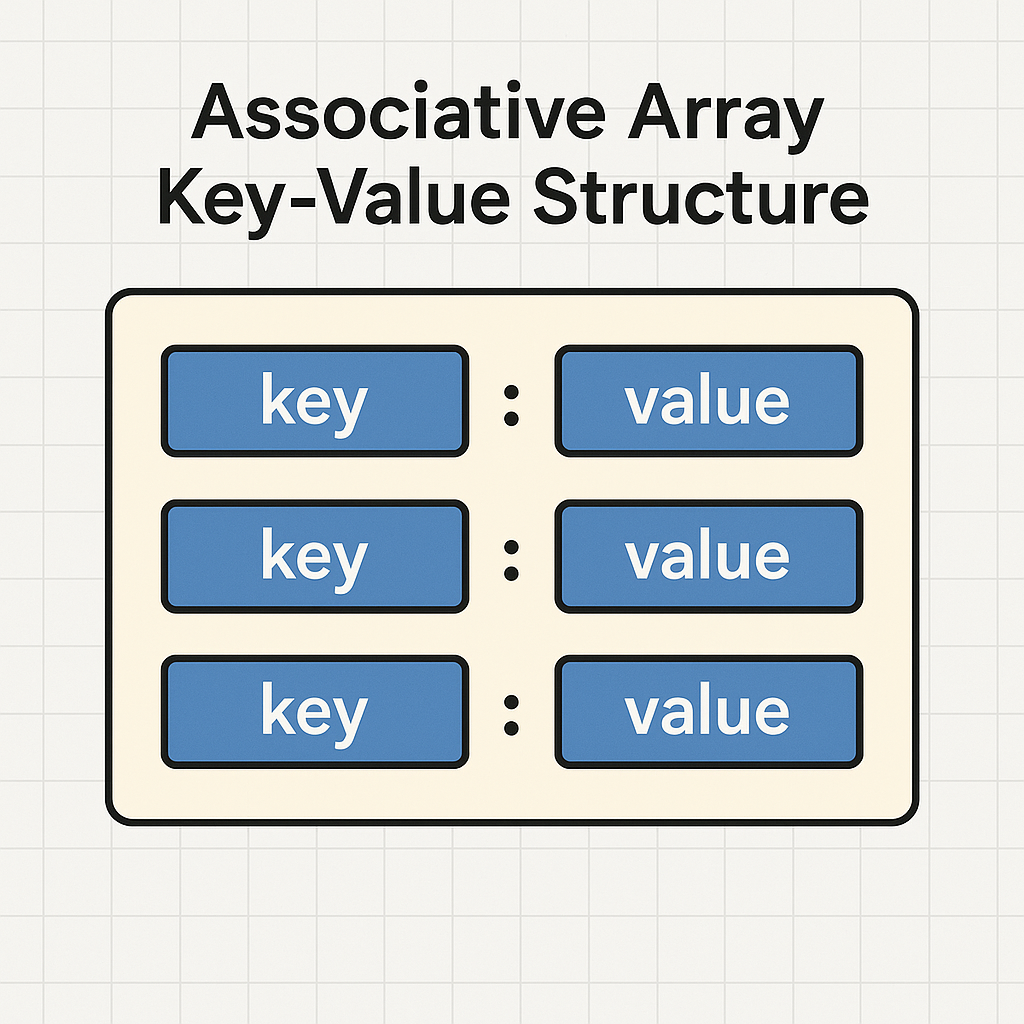
Practical Use Cases
The real power of associative arrays becomes evident in practical applications. They are perfect for managing configuration settings, processing form data from $_POST superglobals, or handling data fetched from an API or database. When a database query returns a single record, it’s often structured as an associative array where column names are the keys and a row’s data are the values. This intuitive mapping makes it simple to extract and use specific pieces of information without relying on their numerical order. We leverage this approach extensively in the custom web applications you can see in Our Work, ensuring our code is both efficient and maintainable.
Multidimensional Arrays: Arrays within Arrays
Building Complex Data Structures
Multidimensional arrays take the concept a step further by allowing you to store arrays within other arrays. This creates a more complex, layered data structure that can represent grids, tables, or hierarchical data. A common example is a two-dimensional array, which can be thought of as a table with rows and columns. You might use one to store a list of products, where each product is itself an associative array containing its name, price, and stock quantity. This allows you to group and manage highly structured, related data within a single variable.
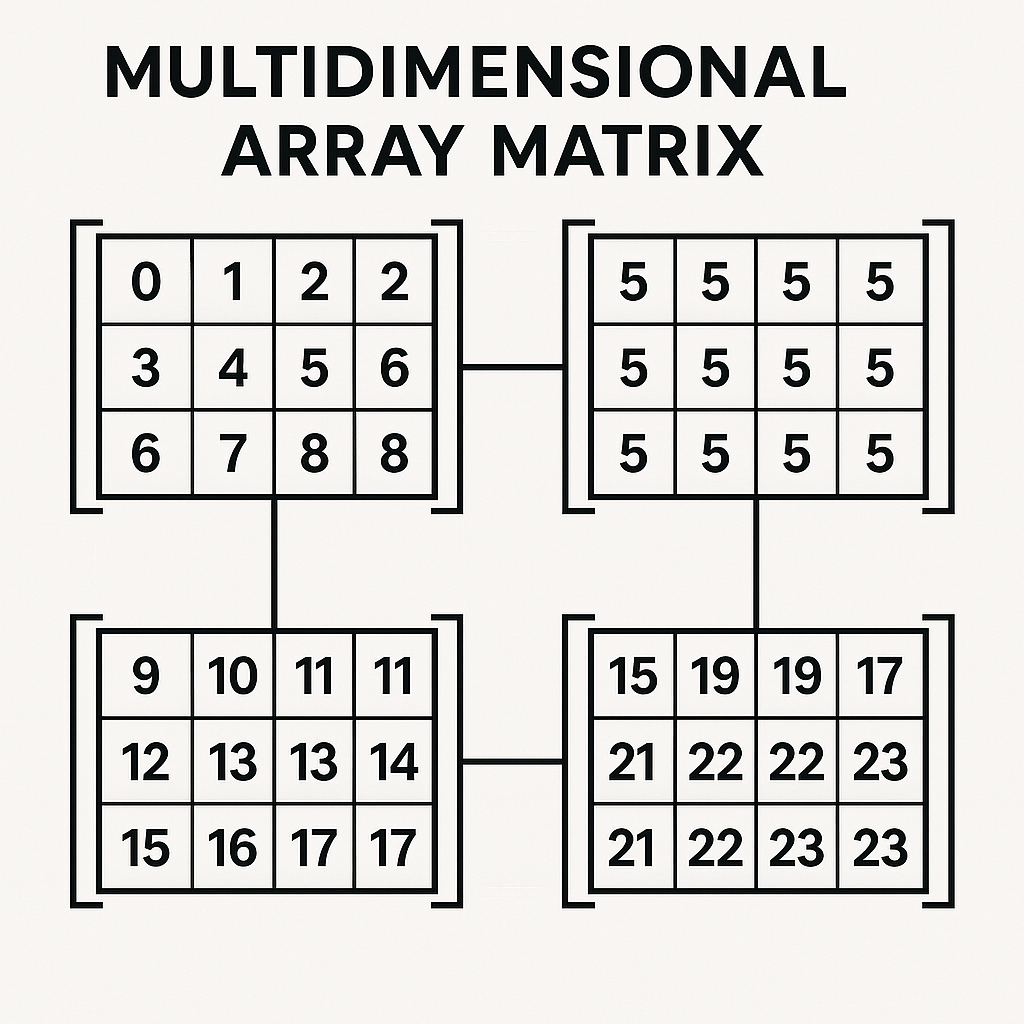
Looping Through Nested Data
Accessing elements in a multidimensional array requires chaining the keys or indices. For a two-dimensional array, you would use a first set of square brackets to specify the “row” and a second set to specify the “column” or inner key. While this can seem complex at first, it provides a powerful way to model real-world data. To process all the data within such a structure, you typically need to use nested loops. A common pattern is to use an outer foreach loop to iterate through the main array (the rows) and an inner foreach loop to iterate through each nested array (the columns or properties).
Essential Array Functions You Must Know
PHP comes with a rich library of built-in functions that make array manipulation incredibly efficient. Instead of writing complex loops to perform common tasks, you can leverage these pre-built tools. Functions for counting elements, adding or removing items, merging multiple arrays, or sorting data are just a few examples. Learning to use these functions effectively is a hallmark of a proficient PHP developer, as it leads to cleaner, more concise, and less error-prone code. They are your best friend for handling data transformations and inquiries quickly.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
count() |
Returns the number of elements in an array. |
array_push() |
Adds one or more elements onto the end of an array. |
array_pop() |
Removes and returns the last element of an array. |
array_merge() |
Merges one or more arrays into one. |
in_array() |
Checks if a specified value exists in an array. |
sort() |
Sorts an array in ascending order. |
For a complete list, the official PHP array documentation is an indispensable resource.
Practical Application and Further Learning
Arrays are not just a theoretical concept; they are used everywhere in real-world web development. When a user submits a form on your website, the data is collected into the $_POST or $_GET superglobal arrays. When you fetch a list of articles from your database to display on a blog, the result is almost always an array of associative arrays. Understanding how to handle these structures is non-negotiable for building dynamic websites. Practice is key to building confidence.
Try creating your own arrays and manipulating them with different functions. As you become more comfortable, you’ll see how they form the backbone of countless web application features. Explore open-source projects on platforms like GitHub or read tutorials on Smashing Magazine to see arrays in action. At Lucid Site Designs, we believe in building robust and scalable applications, and that process always starts with a solid foundation in fundamental data structures like arrays. If you are ready to apply these concepts to a real project or need expert guidance, we encourage you to Contact Us.

Leave a Reply