The Foundation of Reliable User Input
Web forms are the primary channel for user interaction and data collection on any website, from a simple contact form to a complex e-commerce checkout. Ensuring the data submitted through these forms is accurate, complete, and properly formatted is crucial for both data integrity and a positive user experience. While HTML5 provides native validation attributes, they often lack the flexibility and sophisticated logic required for modern applications. This is where the jQuery Validate plugin excels, offering a robust framework for both standard and highly customized validation logic. Implementing effective validation prevents bad data from reaching your server, reduces user frustration by providing immediate feedback, and ultimately guides users to successfully complete their tasks. According to the Baymard Institute, 17% of users have abandoned an online purchase solely due to a long or complicated checkout process, a problem that clear, real-time validation directly addresses (Baymard Institute, 2023). Before diving into custom rules, it is essential to have the basic library and plugin in place. You will need to include the core jQuery library followed by the jQuery Validate plugin script in your HTML file, typically just before the closing body tag.
![Image: HTML structure showing script includes for jQuery and jQuery Validate]
Once the scripts are included, you can initialize the validation on any form by selecting it with a jQuery selector and calling the .validate() method. This simple call is enough to enable default validation for standard HTML5 attributes like required or type="email".
Building Custom Validation Logic with addMethod
The true power of the jQuery Validate plugin is unlocked when you move beyond its built-in rules. For scenarios requiring specific formats, business logic, or external checks, you must create your own rules. The plugin provides a straightforward way to do this using the $.validator.addMethod() function. This function is the cornerstone of custom validation, allowing you to define a reusable rule that can be applied to any form element on your site. Understanding its structure is the first step toward mastering form validation.
The addMethod Syntax
The $.validator.addMethod() function accepts three parameters: the name of your new rule, the validation function itself, and a default error message. The validation function receives the current value of the form element, the element itself, and any parameters you pass to the rule. This function must return true if the element’s value is valid and false if it is not. The message parameter is a string that will be displayed to the user when validation fails, and it can include placeholders for any parameters passed to the rule.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
String | The unique name for your custom validation rule (e.g., ‘strongPassword’). |
method |
Function | The callback function that performs the validation logic. Returns true for valid, false for invalid. |
message |
String | The default error message to display when validation fails. |
Practical Example: A Strong Password Rule
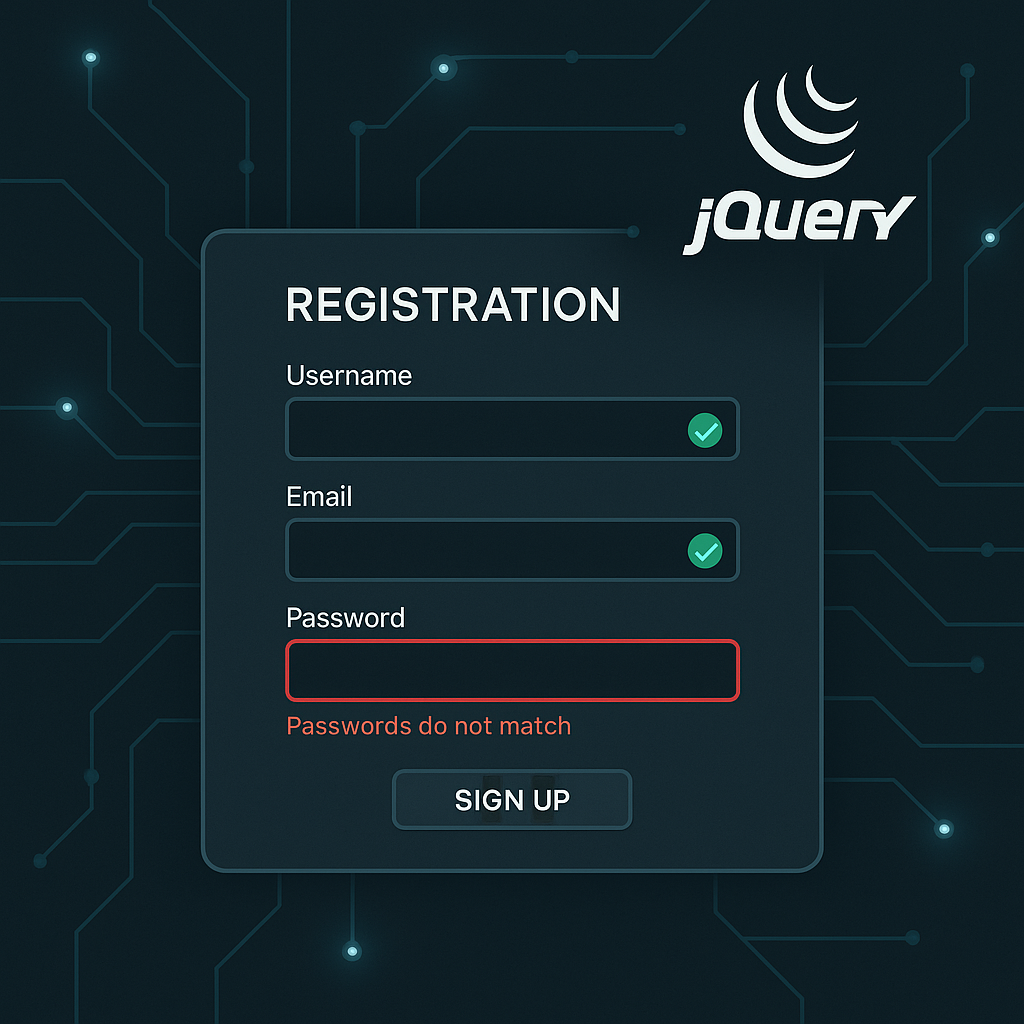
A common requirement is to enforce a strong password policy. For instance, you might require a password to be at least eight characters long and contain a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers. While the plugin has a minlength rule, the character composition check requires a custom method. We can define a rule called strongPassword that uses a regular expression to test the password’s complexity. This approach provides immediate, client-side feedback to the user as they type, helping them create a secure password without a frustrating trial-and-error submission process. This enhances security and improves the user’s journey.
![Image: Code snippet for a custom password validation rule]
Advanced Example: Real-time Username Availability with AJAX
Another powerful application of custom validation is checking for unique values, such as a username or email address, against your database. This prevents users from signing up with an identifier that is already taken. This can be accomplished by creating a custom rule that makes an asynchronous (AJAX) request to a server-side script. The script checks the database and returns a response, typically true or false, indicating availability. The jQuery Validate plugin handles asynchronous rules gracefully, waiting for the server’s response before completing validation. This gives the user instant feedback on their chosen username, which is a significant improvement over waiting until they submit the entire form.
Applying and Customizing Your New Rules
Once you have defined your custom methods using $.validator.addMethod(), you need to apply them to your form fields. This is done within the rules object when you initialize the validator with the .validate() method. For each field you want to validate, you specify the rules that apply. For our custom strongPassword rule, you would simply add strongPassword: true to the rules for the password input field.
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
required |
Makes the element required. |
email |
Requires the element to have a valid email format. |
minlength |
Requires the element to have a minimum length. |
equalTo |
Requires the element to have the same value as another element. |
remote |
Performs a remote (AJAX) validation. |
You can also override the default error messages on a per-field basis using the messages object. This allows you to provide more context-specific feedback. For example, instead of a generic “Please enter a valid value,” you could say, “Your password must contain at least one number and one uppercase letter.” Clear, helpful messages are a critical component of a user-friendly form. The documentation for the jQuery Validate plugin provides a comprehensive list of all configuration options. You can also test your regular expressions using a tool like RegExr to ensure they work as expected before implementing them.
![Image: Diagram showing client-side vs. server-side validation flow]
It is imperative to remember that client-side validation is a UX enhancement, not a security measure. A malicious user can easily bypass any JavaScript-based checks. Therefore, server-side validation is absolutely essential and non-negotiable. Always re-validate all incoming data on your server before processing it or storing it in a database. This dual-layered approach ensures both a smooth user experience and a secure application. This is a core principle in our approach to Web Marketing and application development. For more information on web development best practices, you can review the MDN Web Docs.
By mastering custom validation rules with jQuery, you can transform standard HTML forms into intelligent, interactive, and user-friendly data collection tools. This not only improves the quality of the data you receive but also significantly enhances the overall user experience on your site. If you’re looking to implement robust and secure forms on your website, our team at Lucid Site Designs has the expertise to build solutions that work. For a consultation on how we can improve your web applications, please Contact Us.
Leave a Reply