What is Dart?
Welcome to the world of Dart, the powerful, client-optimized programming language created by Google. Originally conceived to build web, server, and mobile applications, Dart has found its ultimate calling as the language behind the revolutionary Flutter framework. Its core design philosophy centers on providing a flexible, productive, and high-performance environment for building beautiful user interfaces on any screen. Dart combines a familiar C-style syntax, making it easy for developers from backgrounds like Java, C#, or JavaScript to pick up, with modern features that streamline the development process and ensure robust, scalable applications. It is not just a language but a complete platform, including its own libraries, package manager, and development tools.

The Core Strengths of Dart
One of Dart’s most significant advantages is its versatile compilation technology. It uniquely employs both Just-in-Time (JIT) and Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation. During development, JIT compilation allows for incredibly fast development cycles with a feature called stateful hot reload, where code changes are injected into a running app in milliseconds. For production, Dart code is AOT-compiled into fast, predictable, native machine code. This dual-capability means developers get the best of both worlds: the rapid iteration speed of an interpreted language and the high performance of a compiled language, all within a single toolchain.
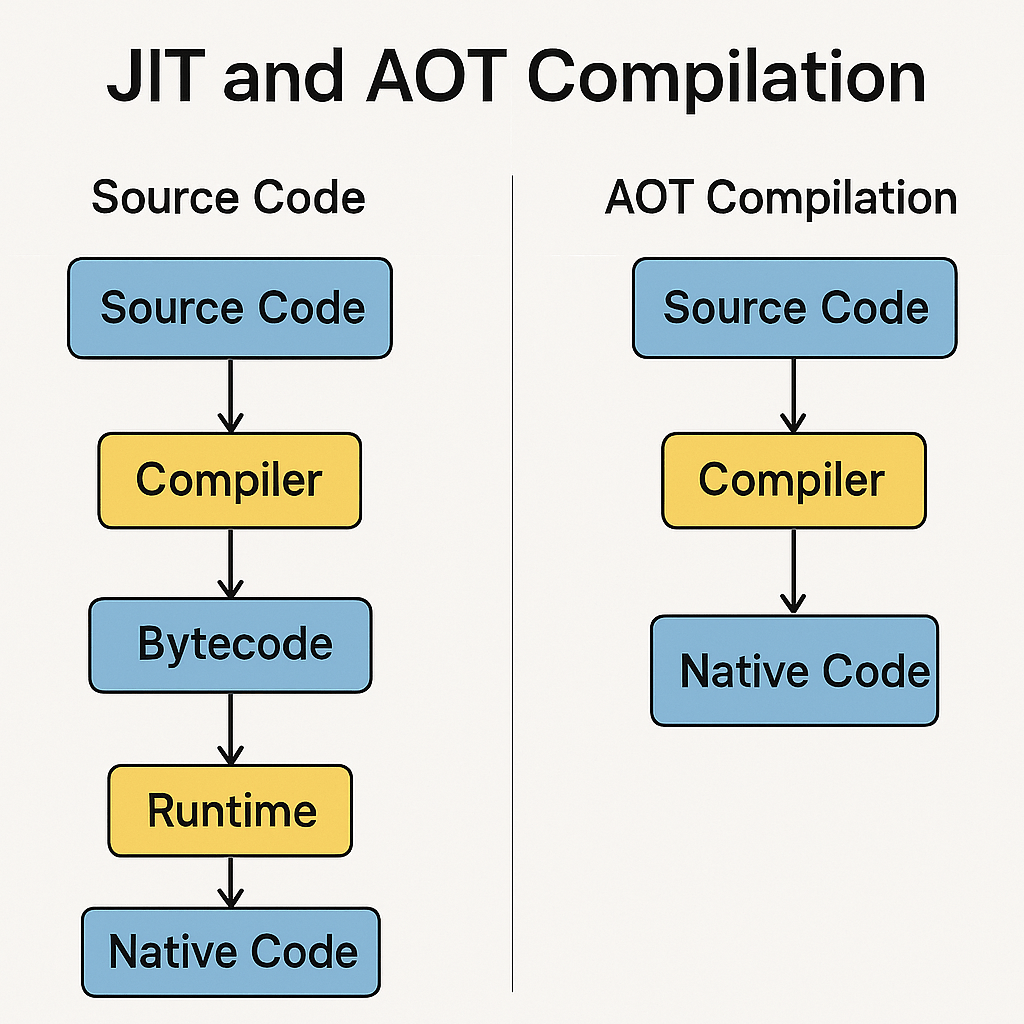
Another cornerstone of the language is its commitment to type safety and sound null safety. Sound null safety, integrated directly into the type system, helps developers avoid a whole class of common errors: the dreaded null pointer exceptions. By differentiating between nullable and non-nullable types, the compiler can catch potential errors before the code even runs. This not only leads to more stable and reliable applications but also allows the compiler to make optimizations that result in smaller and faster code, ensuring your applications are both robust and performant.
Getting Your Development Environment Ready
Getting started with Dart is a straightforward process. The first step is to install the Dart SDK, which you can download directly from the official Dart website. The SDK includes the compiler, a core set of libraries, and the dart command-line tool. For an optimal coding experience, we highly recommend using a modern editor like Visual Studio Code and installing its official Dart extension. This provides essential features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging support. You will also quickly become familiar with the Pub.dev package manager, which is the official repository for Dart and Flutter packages, giving you access to thousands of reusable libraries.
Fundamental Dart Concepts with Examples
Variables and Data Types
At its heart, Dart is a strongly typed language, but it offers flexibility in how you declare variables. You can use the var keyword to let Dart infer the type, or you can be explicit. Key data types include int for integers, double for floating-point numbers, String for text, and bool for true/false values. Dart also provides two important keywords for variables that won’t change: final and const. A final variable can only be set once, while a const variable is a compile-time constant, meaning its value must be known when the code is compiled.
| Keyword | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
var |
A variable whose type is inferred and can be reassigned. | var name = 'Kodeco'; |
final |
A single-assignment variable; once set, it cannot be changed. | final int year = 2024; |
const |
A compile-time constant; its value must be known at compile time. | const double pi = 3.14; |
Beyond these primitives, Dart has powerful built-in support for collections, which are essential for managing groups of data. The two most common collection types you will use are List and Map. A List is an ordered collection of items, similar to an array in other languages. A Map is an unordered collection of key-value pairs, often called a dictionary or hash map. These collections are fundamental for structuring data in any non-trivial application and are deeply integrated into the language.
Functions: The Building Blocks of Logic
Functions are the primary way to organize and reuse code in Dart. A function is a self-contained block of code that performs a specific task. Dart functions can accept parameters and must specify a return type, though void is used if a function doesn’t return a value. For functions that contain just one expression, Dart provides a convenient arrow (=>) syntax, which is a shorthand way to define and return the result of that single expression. This helps keep your code clean, readable, and concise, especially when working with many small, single-purpose functions.
Control Flow Statements
To create dynamic and responsive applications, you need to control the flow of your program’s execution. Dart provides all the standard control flow statements you would expect from a modern language. You use if and else statements to execute code conditionally based on a boolean expression. For iteration, for loops are perfect for running a block of code a specific number of times, especially when iterating over collections like a List. For loops that should continue as long as a certain condition remains true, the while loop is the tool of choice.
A Glimpse into Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Dart is a true object-oriented programming (OOP) language, where everything, including numbers and functions, is an object. An object is an instance of a class, and a class acts as a blueprint for creating objects. Classes bundle data (properties or instance variables) and behavior (methods) into a single, cohesive unit. This paradigm is crucial for building complex, maintainable applications by modeling real-world entities. For example, you could create a Developer class with properties like name and skill and methods like writeCode(). For those looking to master this, we have a resource to help you explore [advanced object-oriented concepts in Dart](URL).

Why You Should Learn Dart Today
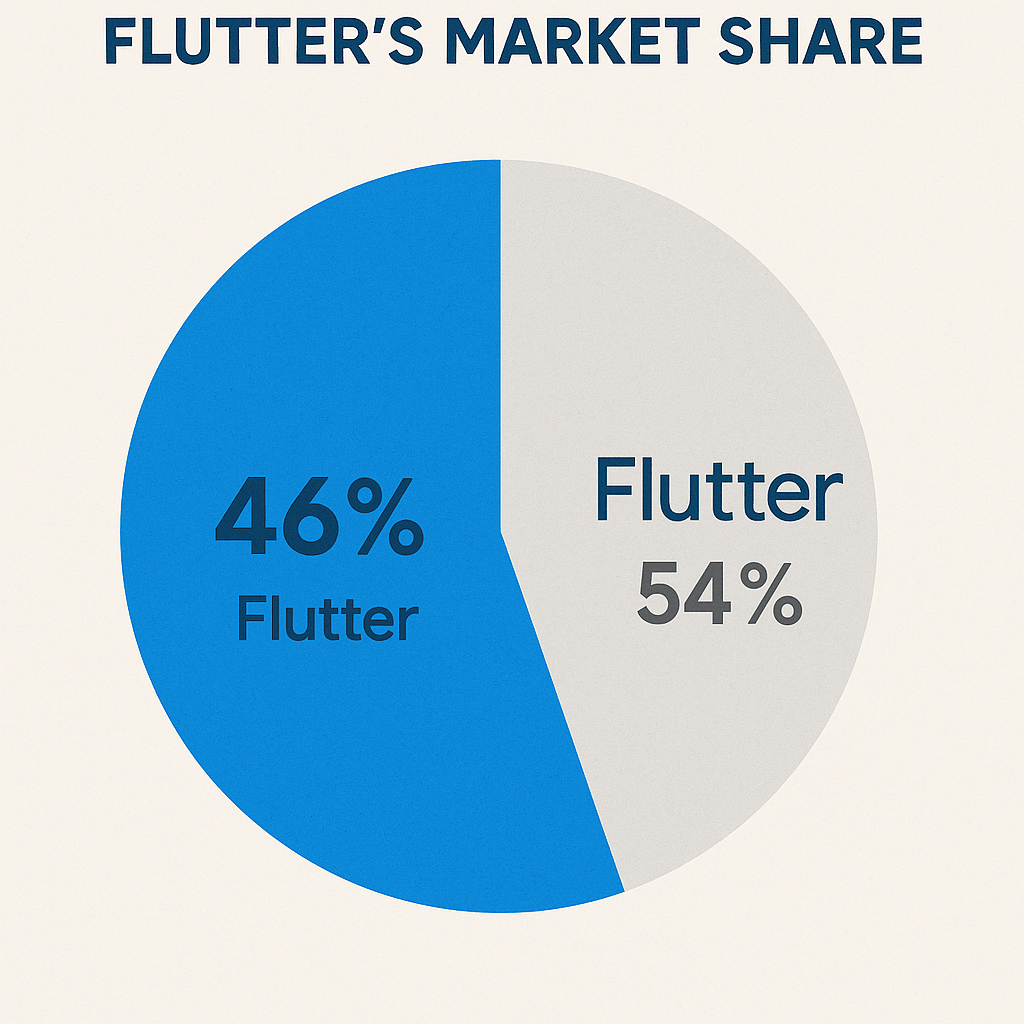
The single biggest reason to learn Dart is its inseparable link to Flutter. As the language powering Flutter, Dart is your gateway to building high-quality, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. The demand for Flutter developers is skyrocketing. According to a 2023 Statista survey, Flutter is the most popular cross-platform mobile framework, used by 46% of software developers worldwide. Mastering Dart positions you at the forefront of this industry trend. You can get started by exploring the official [Flutter documentation](URL).
Beyond Flutter, Dart offers an exceptional developer experience. The language is designed to be productive and enjoyable. Features like the aforementioned stateful hot reload dramatically shorten the edit-test cycle, while its clean syntax and comprehensive standard library make writing code a pleasure. The built-in support for asynchronous programming with async and await makes handling complex operations like network requests simple and readable. If you’re ready for more, you can [deep dive into Dart's asynchronous programming](URL) with our specialized tutorials that cover these powerful features in detail.
Your Next Steps with Dart and Flutter
You’ve now seen a glimpse of what makes Dart a compelling language for modern application development. It offers an unmatched combination of developer productivity, multi-platform reach, and raw performance. Its thoughtful design, coupled with the power of the Flutter framework, provides a clear path for creating beautiful, fast, and consistent experiences across all devices. The journey from learning Dart basics to building sophisticated applications is incredibly rewarding. We encourage you to take the next step and begin your learning adventure today. To get on the fast track, explore [Our comprehensive Flutter learning path](URL), which is designed to guide you from foundational concepts to becoming a proficient Flutter developer.

Leave a Reply